This calculator computes the sample standard deviation or the population standard deviation for any data and shows you how to compute the standard deviation manually. Here’s how it works:
- Enter the data (comma-separated, space-separated, or copy-paste from Excel)
- Select between population and sample standard deviation
- Click the Calculate button
The calculator provides an accurate answer along with an explanation of how to compute the standard deviation by hand.
Enter your data values separated by commas. Example: 2, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 9
What is Standard Deviation?
Standard deviation is a statistical measure of dispersion that quantifies the amount of variability in a dataset. It basically shows how far individual data points deviate from the mean.
Therefore, a small standard deviation means that most values in your dataset lie close to the mean, suggesting low variability. Similarly, a large standard deviation indicates that there’s greater variability within the data.
The two common types of standard deviation are:
- Population standard deviation (σ). It measures how spread out all data points in an entire group (population) are from the average (mean).
- Sample standard deviation (s). It measures how spread out the data points in a sample are from the sample mean.
Population Standard Deviation
The population standard deviation is a measure of dispersion, which tells us how much the entire population vary from the population mean. In statistics, the population standard deviation symbol is a greek letter sigma (σ).
Since every member of the population is studied, we need to divide the deviations from the population mean by N. In this case, N is the total number of observations in the population. Therefore, the population standard deviation formula becomes:
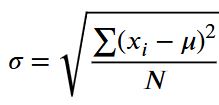
Where:
- σ = population standard deviation
- μ = population mean
- xᵢ = each individual data value
- N = total number of values in the population
- Σ = summation symbol
While the formula may seem complex, its application is very simple. You just need to calculate the average squared deviation of each value from the population mean and find the square root of the results. Let’s learn how to find population standard deviation with an example.
How to Find Population Standard Deviation
To find the population standard deviation, you can use either a manual calculation or an automated approach. In this section, we demonstrate two methods for computing the population standard deviation (σ):
- By Hand (Manual Computation)
- Using the Population Standard Deviation Calculator
Method 1: Find Population Standard Deviation By Hand
Let’s assume you want to find the population standard deviation of the following dataset from a population: 4, 6, 8, 10, 12. To compute the population standard deviation manually, follow the steps:
Step 1: Calculate the Population Mean (μ)
You find the population mean (μ) by adding all data values and dividing the results by the total number of observations (N).
Therefore, the population mean is:
Step 2: Find Each Deviation from the Mean
This steps involves subtracting the mean from each deviation to get the deviations from the mean (xi−μ). You can use a table for simplicity as shown below:
| Observation (xi) | Deviation from the mean (xi−μ) |
| 4 | 4-8 = -4 |
| 6 | 6-8 = -2 |
| 8 | 8-8 = 0 |
| 10 | 10-8 = 2 |
| 12 | 12-8 = 4 |
Step 3: Square Each Deviation
Here, you need to square each of the deviation to remove the negative values. You’ll find (xi−μ)^2. Thus, we extend the table as follows:
| Observation (xi) | Deviation from the mean (xi−μ) | Square the deviations (xi−μ)^2 |
| 4 | 4-8 = -4 | (-4)^2 = 16 |
| 6 | 6-8 = -2 | (-2)^2 = 4 |
| 8 | 8-8 = 0 | (0)^2 = 0 |
| 10 | 10-8 = 2 | (2)^2 = 4 |
| 12 | 12-8 = 4 | (4) ^2 = 16 |
Step 4: Compute the Average of the Squared Deviations
Since we already have the squared deviations, we need to find the average of these deviations. Thus, we add all the squared deviations and divide by the total number of observations in the population (N) as shown below:
Step 5: Take the Square Root
The square root of the average squared deviations will give you the population standard deviation. Thus, taking the square root gives:
Therefore, the population standard deviation (σ) for the data set 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 is approximately 2.83.
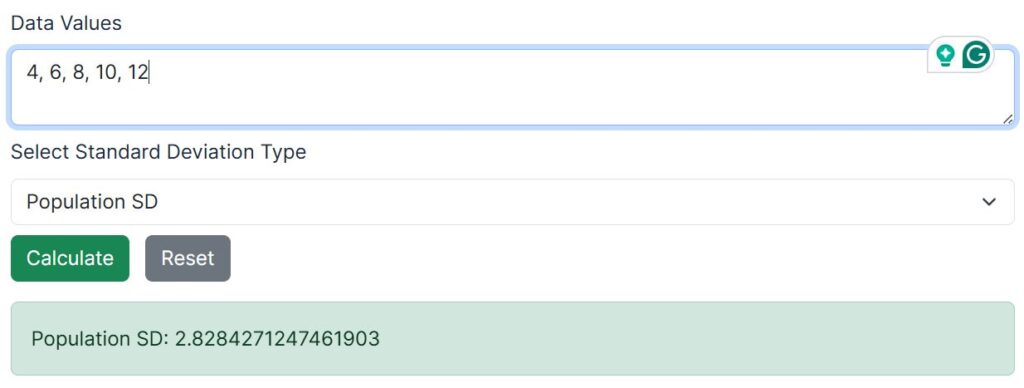
Method 2: Using the Population Standard Deviation Calculator
To compute the population standard deviation of the same data using the calculator, simply follow these steps:
- Enter all population data values into the input field and separate the values either using comma or spaces
- Select Population Standard Deviation (σ) as the calculation type.
- Click the Calculate button.
The calculator will instantly return the population standard deviation as 2.8284. It will also provide a clear explanation of each computation step to help you learn how to apply the population standard deviation formula.
NOTE: You should only use the population standard deviation when:
- The dataset includes all members of the population
- No inference about a larger group is required
- The data represent complete records, such as all employees in a company or all test scores in a class
Sample Standard Deviation
The sample standard deviation is a measure of dispersion that describes how much the values in a sample vary from the sample mean. It is used when the data represent only a subset of a larger population. In statistics, the sample standard deviation symbol is s.
Unlike the population standard deviation which includes all members in the target population, the sample standard deviation only include a subset of this population. To correct for potential bias, we need to divide the squared deviations by n-1, where n is the total number of observations in the sample data. This adjustment is known as Bessel’s correction.
Therefore, the sample standard deviation formula becomes:
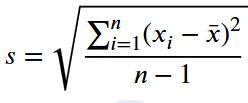
Where:
- s = sample standard deviation
- x̄ = sample mean
- xᵢ = each individual data value
- n = total number of observations in the sample
- Σ = summation symbol
Although the formula may appear complex, its application follows the same logical steps as the population standard deviation. The only difference difference is the use of n − 1 in the denominator. Let’s learn how to find the sample standard deviation with an example.
How to Find Sample Standard Deviation
To find the sample standard deviation, you can use either a manual calculation or an automated approach. In this section, we demonstrate two methods for computing the sample standard deviation (s):
- By Hand (Manual Computation)
- Using the Sample Standard Deviation Calculator
Method 1: Find Sample Standard Deviation By Hand
Suppose you want to compute the sample standard deviation for the following dataset drawn from a larger population:
Sample data: 4, 6, 8, 10, 12
To compute the sample standard deviation manually, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Calculate the Sample Mean (x̄)
To find the sample mean of the dataset, you need to add all data values and divide the results by the total number of observations in the sample (n). Thus, the sample mean is:
Step 2: Find Each Deviation from the Sample Mean
Subtract the sample mean from each data value to obtain the deviations (xi−x̄).
| Observation (xᵢ) | Deviation from the mean (xᵢ − x̄) |
|---|---|
| 4 | 4 − 8 = −4 |
| 6 | 6 − 8 = −2 |
| 8 | 8 − 8 = 0 |
| 10 | 10 − 8 = 2 |
| 12 | 12 − 8 = 4 |
Step 3: Square Each Deviation from the Sample Mean
Square each deviation to eliminate negative values. Thus, we extend the table as follows:
| Observation (xᵢ) | (xᵢ − x̄) | (xᵢ − x̄)² |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | −4 | 16 |
| 6 | −2 | 4 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 2 | 4 |
| 12 | 4 | 16 |
Step 4: Compute the Average of the Squared Deviations from the Sample Mean
Add all squared deviations and divide by n − 1 (since this is sample data). Thus, the average of the squared deviations becomes:
Step 5: Take the Square Root of the Results
The square root of average squared deviation gives the sample standard deviation. Thus, the sample standard deviation is:
Therefore, the sample standard deviation (s) for the dataset 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 is approximately 3.16.
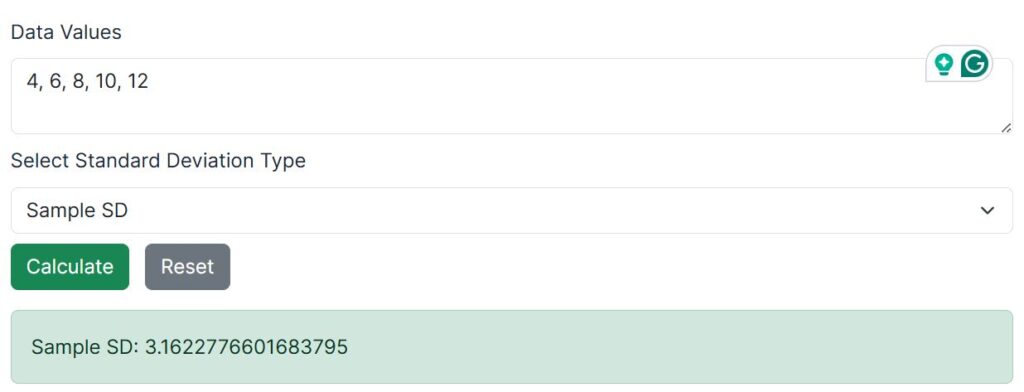
Method 2: Using the Sample Standard Deviation Calculator
To compute the sample standard deviation of the same data using the calculator, follow these steps:
- Enter the sample data values into the input field, separated by commas or spaces.
- Select Sample Standard Deviation (s) as the calculation type.
- Click the Calculate button.
The calculator will instantly return the sample standard deviation as 3.1623. You’ll also find a clear explanation of each computational step to help you learn how to apply the sample standard deviation formula.
NOTE: You should use the sample standard deviation when:
- The data represent a subset of a larger population
- You intend to make inferences about the population
- The population standard deviation is unknown
